Analyzing cell populations in whole blood is a fundamental yet challenging task. Even after standard preparation steps, samples often contain mixed populations of leukocytes, platelets, and red blood cells (RBCs). Cytely enables researchers to rapidly identify and quantify these populations at the single-cell level. Through scatter plots and intuitive gating, different blood cell types can be distinguished and characterized in an unbiased, interactive workflow. Key features demonstrated in this note: Visualizing heterogeneity across a mixed cell population Identifying populations (neutrophils, platelets, RBCs) using scatter plots Gating to isolate neutrophil subsets
Downloadable Files
Identifying Contaminants in Neutrophil Preparations
Analyzing cell populations in whole blood is a fundamental yet challenging task. Even after standard preparation steps, samples often contain mixed populations of leukocytes, platelets, and red blood cells (RBCs). Cytely enables researchers to rapidly identify and quantify these populations at the single-cell level. Through scatter plots and intuitive gating, different blood cell types can be distinguished and characterized in an unbiased, interactive workflow.
Key features demonstrated in this note:
- Visualizing heterogeneity across a mixed cell population
- Identifying populations (neutrophils, platelets, RBCs) using scatter plots
- Gating to isolate neutrophil subsets
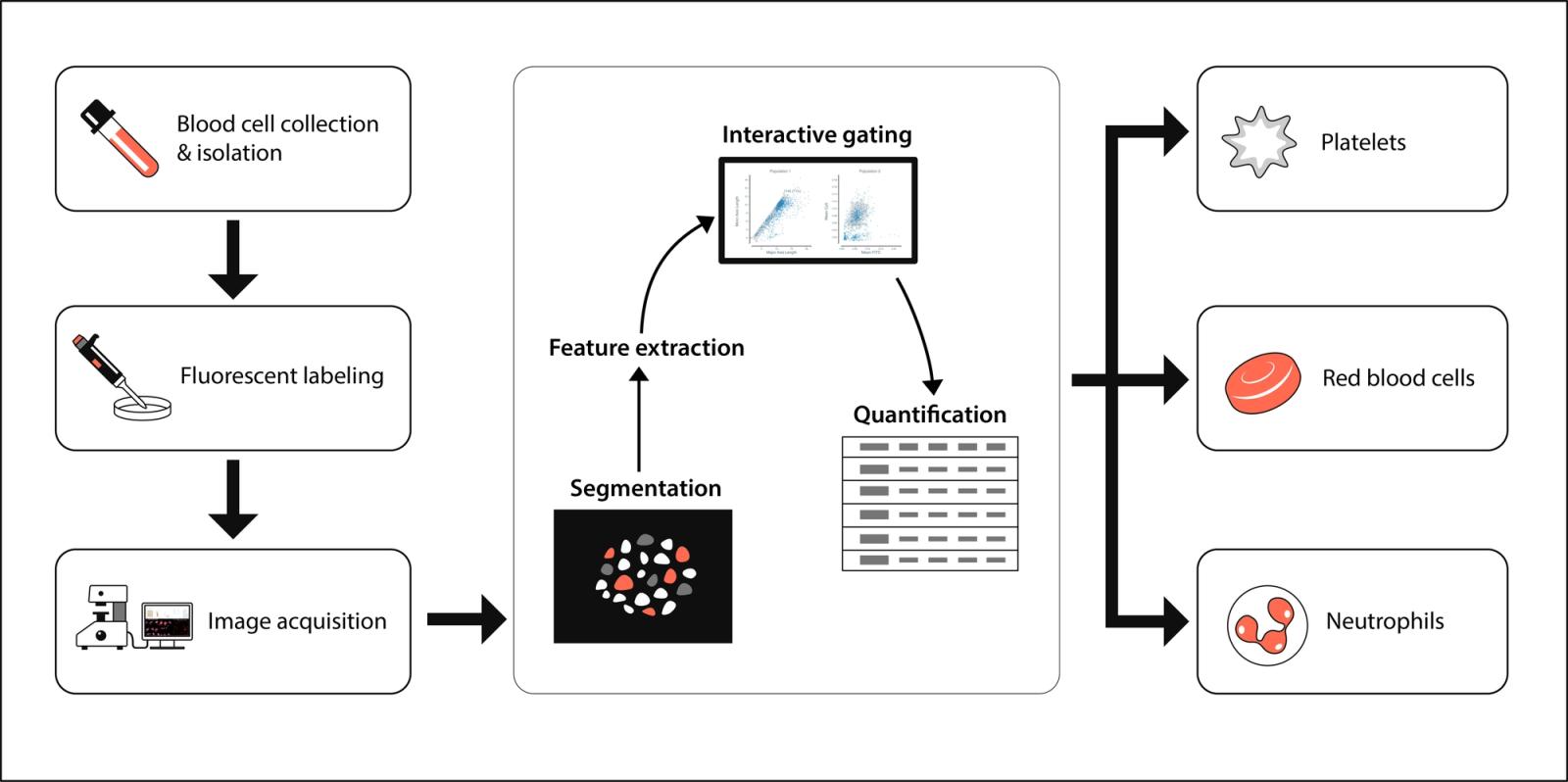
Experimental Method
Blood collection and neutrophil isolation
Peripheral blood was obtained from a healthy volunteer by venipuncture using a butterfly needle and collected into sodium citrate anticoagulant tubes. Neutrophils were isolated by density gradient centrifugation using Ficoll-Paque (GE Healthcare), following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Cell handling and staining
Isolated neutrophils were resuspended in Hepes-buffered saline (HBS) (20 mM Hepes, 150 mM NaCl, 2 mM CaCl₂, 1 mM MgCl₂, pH 7.4) and maintained on ice until use.
For fluorescent labeling, cells were incubated for 30 minutes in the dark at room temperature with:
- CellMask™ Green Plasma Membrane Stain (2 µM, Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- CellTracker™ Deep Red (1 µM, Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- Hoechst 33342 nuclear stain (5 µg/mL)
Slide preparation
Whole blood cells were resuspended in PBS and seeded into Ibidi 8-well chamber slides (Ibidi GmbH) for imaging and subsequent analysis in Cytely.
Data Analysis in Cytely
The dataset was analyzed using Cytely’s drag-and-drop interface.
- Upload: Images were uploaded directly via Cytely’s web interface.
- Segmentation: Automated detection of nuclei and cytoplasm.
- Feature extraction: Morphological and intensity parameters (size, shape, channel intensities) computed per cell.
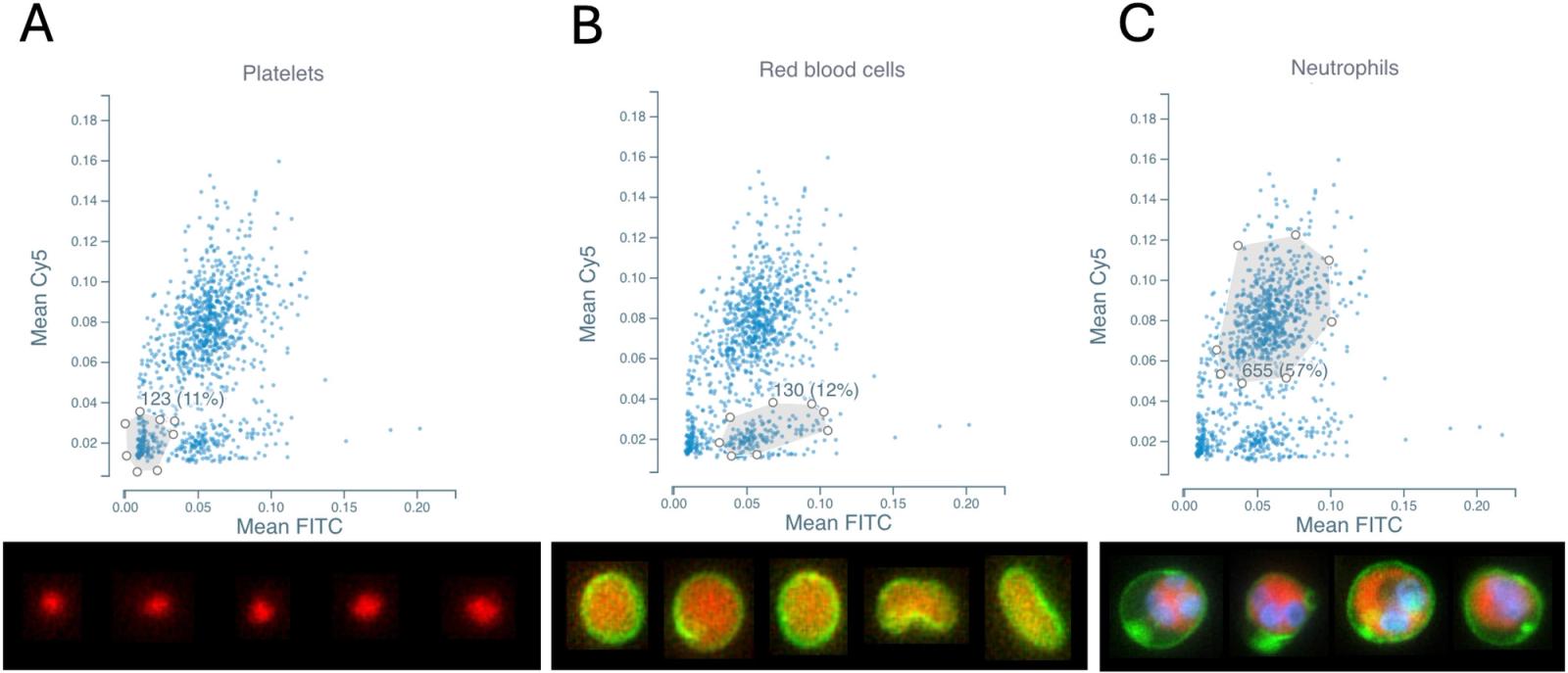
- Scatter plots: Plotting forward scatter proxies (size, morphology) vs. intensity values separated major populations (Figure 1).
- Gating: Neutrophils, RBCs, and platelets were identified based on scatter characteristics (Figure 1).
- Neutrophils: larger, multi-lobed nuclei, strong cytosolic signal
- Platelets: very small, faint membrane and nuclear signal
- RBCs: anucleated, strong membrane signal, little/no Hoechst
- Statistics: Neutrophils were isolated and relevant parameters from the population were extracted (Figure 2).
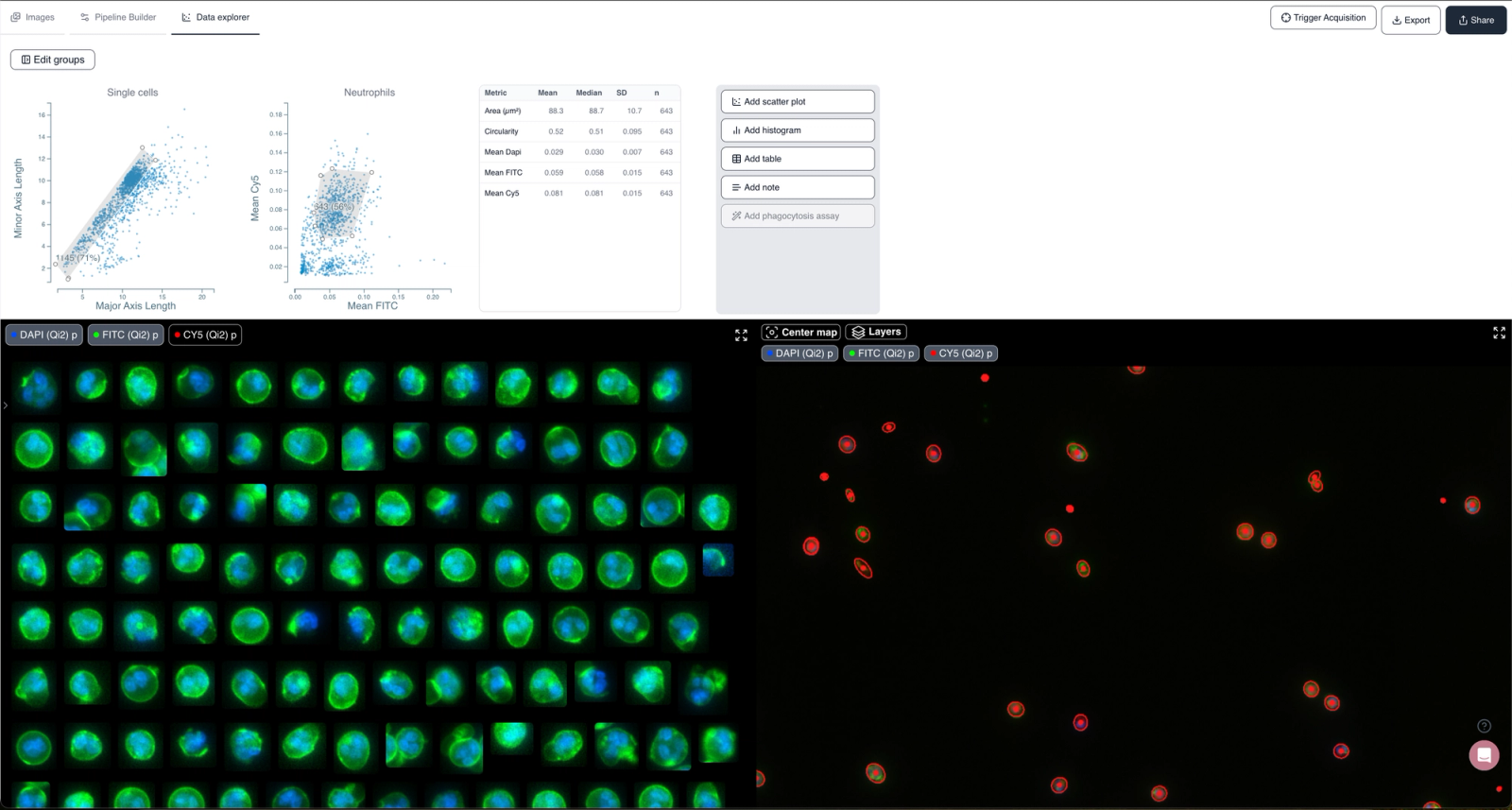
Results and Discussion
- Identification of contaminants: RBCs and platelets were clearly separated from neutrophils (Figure 1).
- Purification outcome: Simple sequential gates excluded contaminants, yielding a clean neutrophil dataset (Figures 2).
- Practical impact: Cytely enables real-time purity assessment and quantification of contaminants without additional assays.
Conclusion
Cytely transforms blood cell analysis by delivering fast, intuitive, and unambiguous assessment of diverse cell populations. Its powerful combination of automated segmentation and scatter-based gating not only quantifies contaminant fractions with precision but also provides immediate visual confirmation of purified subsets — all within a single streamlined workflow. With Cytely, what typically requires multiple downstream assays is reduced to one effortless step, yielding reproducible, publication-ready data with unmatched clarity and confidence.
